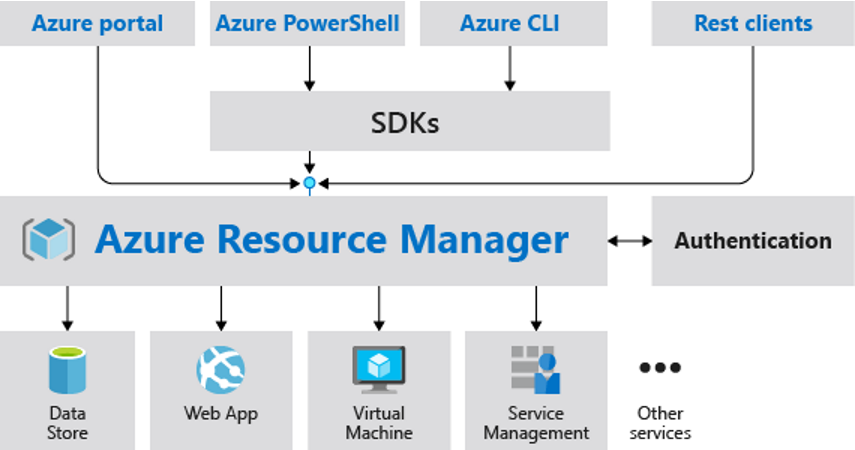
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) is the deployment and management service used by Microsoft Azure. Any action performed in Azure — whether through the Portal, CLI, or PowerShell — is processed through ARM. It provides the management layer for creating, updating, and deleting Azure resources
Functions of Azure Resource Manager
ARM enables administrators to:
- Create resources such as virtual machines, networks, and databases
- Update existing resources according to changing requirements
- Delete resources that are no longer in use
ARM Templates and Infrastructure as Code
One of the core advantages of ARM is its support for Infrastructure as Code (IaC). Rather than configuring resources manually, administrators can use declarative ARM Templates written in JSON to define and deploy infrastructure consistently.
Benefits of ARM Templates include:
- Deployment of standardized environments across multiple regions and projects
- Version control alongside application code for improved change management
- Automation of recurring deployments, reducing configuration errors
For detailed syntax guidance, see the Microsoft documentation on ARM Template syntax.
Bicep Language
Bicep is a domain‑specific language (DSL) designed to simplify the authoring of ARM templates. It compiles directly to ARM JSON templates and provides a more concise and human‑readable syntax.
Key benefits of Bicep:
- Requires less code compared to JSON ARM Templates
- Easier to read and maintain
- Fully integrated with ARM, supporting all features available in ARM Templates
More information is available in the Microsoft Bicep overview.
ARM and Bicep Together
ARM and Bicep are not competing technologies. Bicep is a higher‑level authoring language that compiles into ARM JSON templates. Organizations using ARM Templates can continue to do so or gradually adopt Bicep for improved readability and maintainability.
Conclusion
Azure Resource Manager underpins all actions performed within Azure. Leveraging ARM Templates or Bicep enables consistent, automated, and reliable deployments through Infrastructure as Code practices. Adopting these approaches from the outset helps ensure scalability and reduces configuration errors.
Leave a Reply