Deploying virtual machines (VMs) in Azure requires more than initial provisioning. To ensure workloads remain scalable, reliable, and resilient against failures or demand spikes, Azure provides two core mechanisms: Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS) and Availability Sets. Each addresses different aspects of availability and scalability.
Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS)
VM Scale Sets manage groups of identical VMs, enabling automatic scaling to match workload requirements. They are designed for scenarios with variable or unpredictable demand.
Key characteristics:
- Uniformity: All VMs are created from a single base image, ensuring consistency.
- Group Management: Scale sets are managed as a unit, rather than individually.
- Automatic Scaling: Azure dynamically adjusts the number of VMs in response to demand.
- Integrated Load Balancing: A load balancer is automatically deployed to distribute traffic across the VMs.
Important: Individual VM modifications within a scale set are not recommended. Updates should be applied by modifying the master image and redeploying. The scale set service itself is free of charge; however, compute, storage, and networking resources consumed by the VMs incur costs.
Availability Sets
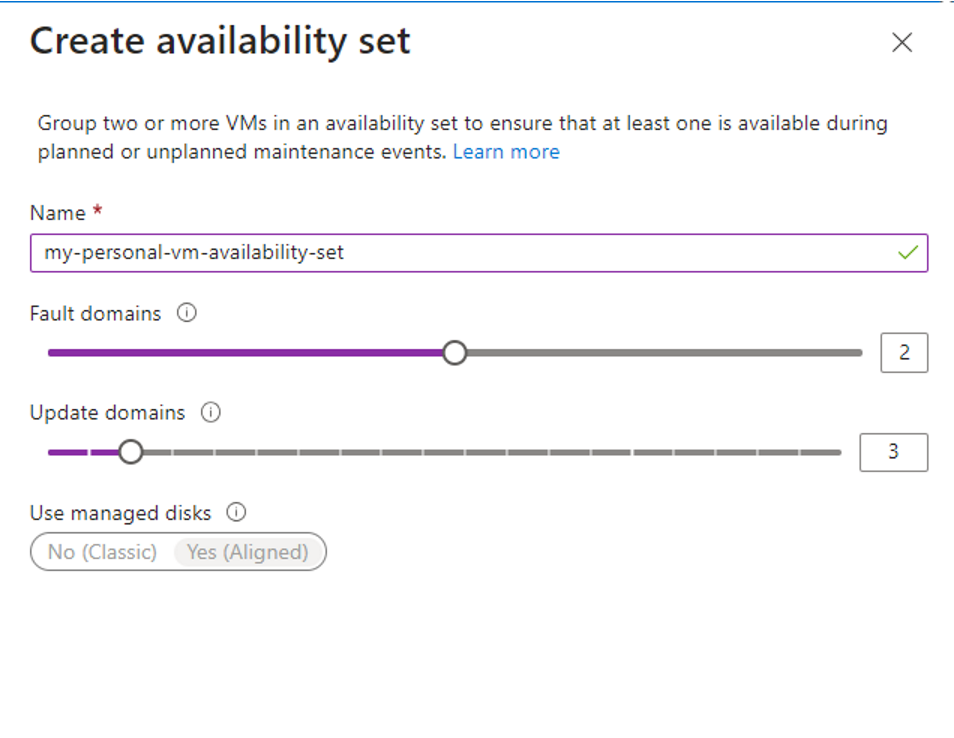
Availability Sets improve resilience by distributing VMs across separate update domains and fault domains within a region.
Key concepts:
- Update Domains: Groups of VMs that may be restarted simultaneously during planned maintenance. Staggering updates ensures that not all VMs are rebooted at the same time.
- Fault Domains: Groups of VMs that share a common power source and network switch. Azure typically distributes VMs across up to three fault domains to minimize the impact of localized hardware failures.
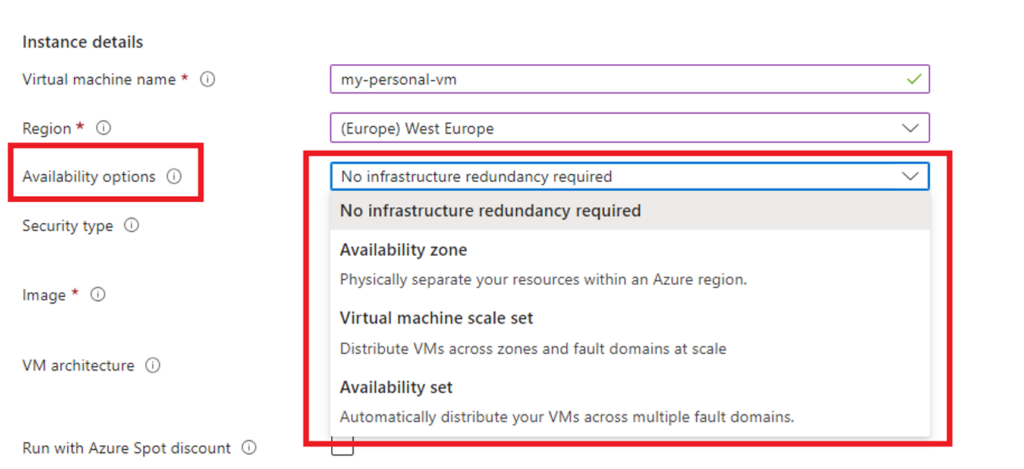
Availability Zones extend this approach further by placing VMs in physically separate datacenters within the same Azure region. Each zone acts as an independent update and fault domain, providing protection against complete datacenter outages and offering a higher Service Level Agreement (SLA) for uptime.
Availability Sets and Availability Zones do not incur additional charges; costs apply only to the deployed VMs and their resources.
VMSS vs. Availability Sets
Selection depends on workload requirements:
- VM Scale Sets (VMSS): Recommended for applications that must dynamically scale, such as web services experiencing variable demand.
- Availability Sets: Appropriate for maintaining high availability in steady workloads, ensuring redundancy across fault and update domains.
- Availability Zones: Best suited for mission‑critical workloads requiring resilience against complete datacenter failures.
Conclusion
Azure offers multiple strategies for scaling and ensuring the availability of virtual machines. VM Scale Sets address automatic scaling needs, while Availability Sets and Availability Zones provide protection against downtime from planned maintenance and infrastructure failures. For mission‑critical workloads, combining VMSS with Availability Zones maximizes both scalability and resilience.
nce.